Important things every U.S. worker abroad should know about the FEIE Standard Deduction
Discovering the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion and How It Associates with Your Basic Deduction
The Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE) provides a substantial chance for migrants to lower their U.S. tax obligation liability. Comprehending the eligibility requirements and determining international gained income is crucial. However, this exclusion makes complex the selection in between claiming the standard reduction and making best use of tax benefits. Maneuvering with these complex regulations can bring about considerable economic effects. What methods can people utilize to enhance their tax situation while continuing to be compliant with IRS regulations?
Recognizing the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE)
Although lots of united state citizens working abroad might face intricate tax commitments, the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) provides considerable relief by permitting eligible individuals to leave out a portion of their foreign earnings from united state taxes. This stipulation is designed to ease the financial concern of double tax on income made in foreign countries. By making use of the FEIE, qualified taxpayers can exclude up to a defined limitation of international made income, which is readjusted yearly for inflation. The exemption applies just to income originated from work or self-employment in an international nation and does not cover various other sorts of earnings, such as financial investment revenue. To gain from the FEIE, people must file the appropriate tax obligation forms with the IRS and guarantee conformity with specific needs. Eventually, the FEIE acts as an essential tool for united state citizens steering the intricacies of worldwide taxation while living and functioning abroad.
Eligibility Requirements for the FEIE
To get the Foreign Earned Earnings Exemption (FEIE), people must fulfill specific requirements developed by the IRS. Initially, they should have foreign made income, which describes wages, incomes, or specialist costs received for solutions done in a foreign nation. Furthermore, the taxpayer should either be an authentic homeowner of a foreign nation or satisfy the physical presence test, which requires spending at the very least 330 complete days in an international country throughout a 12-month duration.
The taxpayer should submit Type 2555 or Kind 2555-EZ to declare the exemption. It is also crucial to note that the FEIE uses just to income earned while residing outside the United States; subsequently, any kind of earnings from united state sources or for solutions carried out in the united state does not certify. Comprehending these eligibility requirements is important for people looking for to profit from the FEIE.
Calculating Your Foreign Earned Revenue
Computing foreign made revenue is vital for individuals looking for to gain from the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion - FEIE Standard Deduction. This process includes recognizing the definition of international earned revenue and the details qualification requirements that apply. Furthermore, various calculation approaches can be used to properly figure out the quantity eligible for exclusion
Interpretation of Foreign Earned Earnings
Foreign gained earnings encompasses the settlement received by people for solutions executed in a foreign nation. This income can consist of incomes, incomes, perks, and expert charges gained while functioning abroad. It is necessary to keep in mind that foreign gained earnings is not restricted to just pay payments; it can additionally include non-cash advantages, such as real estate allocations or the value of dishes provided by a company. To qualify as international made income, the settlement has to be stemmed from services done in an international area, not from U.S. sources. Understanding this meaning is crucial for people seeking to browse the complexities of tax obligation regulations connected to gaining revenue overseas, especially when thinking about the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption.
Eligibility Demands Explained
Eligibility for the Foreign Earned Income Exemption rests on numerous essential demands that people must meet to assure their earnings certifies - FEIE Standard Deduction. To start with, the specific should have international made income, which is income received for services executed in a foreign nation. Furthermore, they have to meet either the bona fide house test or the physical visibility examination. The authentic house examination requires people to be a homeowner of a foreign country for an uninterrupted duration that consists of a whole tax obligation year. On the other hand, the physical existence examination requires existing in an international country for a minimum of 330 complete days throughout a 12-month period. In addition, taxpayers must submit a legitimate tax obligation return and claim the exemption using Kind 2555
Calculation Methods Review
When identifying the amount of international earned earnings eligible for exclusion, individuals have to consider various estimation methods that properly reflect their revenues. One of the most usual approaches consist of the Physical Presence Examination and the Bona Fide Residence Examination. The Physical Existence Test requires people to be physically present in an international country for at the very least 330 days within a twelve-month duration. Alternatively, the Authentic House Test relates to those look at here now that develop a long-term house in an international nation for a nonstop duration. Each approach has certain requirements that should be met, impacting the amount of earnings that can be excluded. Understanding these calculation methods is crucial for making best use of the advantages of the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion and guaranteeing conformity with internal revenue service laws.
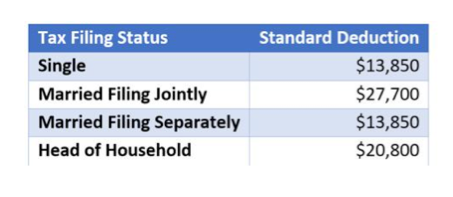
The Function of the Standard Deduction
The common reduction plays a crucial role in specific tax obligation filings, offering taxpayers with a fixed reduction in their gross income. When website link combined with the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion, it can substantially affect the general tax responsibility for migrants. Comprehending just how these two components communicate is vital for enhancing tax obligation benefits while living abroad.
Standard Reduction Overview
Understanding the common deduction is crucial for taxpayers looking for to decrease their gross income. The basic reduction represents a set buck amount that reduces the earnings topic to taxes, streamlining the filing process. It differs based on filing condition-- solitary, wedded declaring collectively, married filing individually, or head of home. For many taxpayers, particularly those without substantial itemized deductions, going with the common deduction might be useful. This reduction is changed yearly for rising cost of living, guaranteeing its relevance in time. By making use of the typical deduction, people can effectively lower their tax obligation liability, making it an essential part of tax planning. Eventually, recognition of the common deduction empowers taxpayers to make enlightened decisions concerning their economic methods.
Communication With Foreign Exemption
Taxpayers living abroad may benefit from both the common reduction and the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption (FEIE) The FEIE permits eligible individuals to omit a significant part of their foreign revenue from united state tax, while the basic reduction decreases gross income for all taxpayers. Significantly, the standard reduction can still apply also when using the FEIE. Taxpayers should keep in mind that the FEIE does not impact the estimation of the typical reduction. For instance, solitary filers can declare the typical reduction amount regardless of their international earnings exclusion. This combination can lead to considerable tax obligation cost savings, allowing expatriates to lessen their total tax obligation liability efficiently while making sure conformity with U.S. tax obligations.
Just How FEIE Impacts Your Common Deduction
Navigating the interplay between the Foreign Earned Income Exemption (FEIE) and the typical reduction can be complex for expatriates. The FEIE enables qualifying people to leave out a particular amount of their international earned income from U.S. tax, which can substantially impact their overall tax obligation responsibility. Nonetheless, it is essential to keep in mind that asserting the FEIE might affect the capacity to use the common deduction.
Specifically, if an expatriate elects to leave out international made income, they can not claim the conventional deduction for that tax year. Instead, they might be qualified for a foreign tax obligation credit, which can be advantageous in certain scenarios. The decision to make use of the FEIE or the basic deduction needs careful consideration of specific scenarios, as it can alter the tax landscape significantly. Recognizing these implications is necessary for migrants looking for to maximize their tax responsibilities while living abroad.
Strategies for Maximizing Your Tax Benefits
While maneuvering with the intricacies of expatriate taxation, people can utilize numerous methods to maximize their tax benefits. One efficient technique entails enhancing the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) by making certain that all qualifying income is properly reported. By timely filing Form 2555, expatriates can exclude a significant section of their income, reducing their total taxable quantity.
Furthermore, individuals ought to consider their residency standing and just how it influences their eligibility for tax benefits. Leveraging available deductions, such as real estate expenses, can even more enhance tax financial savings. Engaging in tax preparation throughout the year, instead of waiting up until tax season, enables expatriates to make informed economic decisions that line up with their tax obligation technique.
Lastly, talking to a tax obligation professional skilled in expatriate tax can supply personalized why not try here understandings, guaranteeing conformity while taking full advantage of offered advantages. Via these approaches, expatriates can efficiently browse the intricacies of their tax responsibilities.
Usual Mistakes to Prevent With FEIE and Reductions
Maximizing the benefits of the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) calls for cautious attention to information to stay clear of usual challenges that can undermine tax cost savings. One constant mistake involves falling short to satisfy the residency demands, which can cause disqualification from the exclusion. One more typical error is incorrectly determining the eligible foreign made revenue, resulting in possible over- or under-reporting. Taxpayers might likewise ignore the need to submit Kind 2555, necessary for declaring the FEIE, or misunderstand the relationship between the FEIE and the typical deduction. It's essential to keep in mind that while the FEIE can lower gross income, it does not affect the common deduction amount, which might trigger confusion. Lastly, overlooking to keep proper documents, such as proof of residency and revenue sources, can complicate audits or future insurance claims. Recognition of these mistakes can help individuals navigate the intricacies of global tax better.
Regularly Asked Questions
Can I Assert FEIE if I Work Remotely for a United State Firm?
Yes, a person can declare the Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption if they work remotely for an U.S. firm, provided they meet the eligibility demands connected to residency and physical visibility in an international nation.
Exactly how Does the FEIE Impact My State Taxes?
The Foreign Earned Revenue Exemption normally does not influence state taxes straight, as rules vary by state. Some states might require locals to report all income, while others align with government exemptions. Private conditions will determine obligation.
Can I Switch Over Between FEIE and the Foreign Tax Debt?
Yes, people can switch over between the Foreign Earned Income Exemption and the Foreign Tax Obligation Credit. Nonetheless, they have to carefully take into consideration the effects and restrictions of each choice for their specific financial circumstance and tax obligation year.
What Occurs if I Surpass the FEIE Income Limit?

Exceeding the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion restriction leads to gross income for the excess amount. This can cause raised tax obligation liability and possible problems in asserting deductions or credit reports associated with international earnings.

Does FEIE Put On Independent Individuals?
Yes, the Foreign Earned Revenue Exclusion (FEIE) relates to independent individuals (FEIE Standard Deduction). They can leave out certifying foreign made revenue, given they satisfy the essential needs, such as the physical visibility or bona fide house examinations
The exemption applies just to revenue obtained from work or self-employment in an international country and does not cover other types of income, such as investment revenue. Determining foreign gained earnings is essential for individuals seeking to benefit from the Foreign Earned Income Exemption. To begin with, the individual have to have international made revenue, which is income obtained for solutions performed in an international nation. The FEIE enables eligible individuals to leave out a significant part of their foreign earnings from U.S. taxes, while the conventional reduction minimizes taxable revenue for all taxpayers. One efficient method entails maximizing the Foreign Earned Earnings Exclusion (FEIE) by ensuring that all qualifying earnings is accurately reported.